问题
如果代码中发生了异常,但我们没有用try/catch捕获,JVM会如何处理?
这是一段肯定会发生异常的代码,但我们没有处理异常,运行这个代码会发生什么?
1 | public class Main { |
程序结束,并且控制台输出下面的内容:
1 | Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero |
这是如何背后的逻辑是什么,为什么会输出这些内容呢?
JAVA异常体系
首先来复习一下JAVA的异常体系。
异常分类
异常继承结构大致如下:
JAVA中所有的异常都是继承自Throwable类。可以分为以下两类:
- 非检查异常(
unchecked exceptions),包括以下两种:- 错误(
Error),包括Error类及其子类。这种异常是在正常情况下,不大可能出现的情况,绝大部分的Error都会导致程序(比如JVM自身)处于非正常的、不可恢复状态。既然是非正常情况,所以不便于也不需要捕获,常见的比如OutOfMemoryError类。 - 运行时异常(
RuntimeException),包括RuntimeException类及其子类。这种异常通常是可以通过编码避免的逻辑错误,具体根据需要来判断是否需要捕获,并不会在编译期强制要求。
- 错误(
- 受检查异常(
checked exception),除了上面两种(Error类及其子类,RuntimeException类及其子类),其他异常都属于受检查异常。这种异常通常是外部错误,不是代码逻辑的错误,编译器强制要求对这种异常进行处理,比如网络连接错误会抛出IOException,我们应该提前预料这种情况并对其进行处理(比如重试)。
异常处理
JAVA中处理异常的方式有两种:
- 使用
try/catch捕获异常并进行处理。 - 使用
throws关键字,在方法上声明可能会抛出的异常,由外层调用者去处理这个异常。
上面两种异常中,受检查异常必须被捕获,否则会编译失败,而非检查异常在编译期不强制要求被捕获。
未捕获异常
如果一个非检查异常没有被捕获处理,那这就是未捕获异常。因为受检查异常都必须在代码中捕获进行处理,所以未捕获异常实际上都是在说非检查异常。
在探究如何处理未捕获异常之前先来看一个接口,这个接口是处理未捕获异常的关键接口:
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler接口
1 |
|
这个接口很简单,只有一个方法,用来处理未捕获的异常,参数是线程信息,以及异常信息,
下面从源码层面来看看如何处理未捕获异常。
未捕获异常处理流程
Thread类中有一个dispatchUncaughtException方法,这个方法的作用是分发异常信息到正确的UncaughtExceptionHandler。当线程运行中出现了未捕获的异常,JVM会调用线程的这个方法,来寻找一个UncaughtExceptionHandler处理异常。
1 | /** |
getUncaughtExceptionHandler的获取逻辑是,如果此线程的uncaughtExceptionHandler属性不为null,则分发异常到线程自己的uncaughtExceptionHandler,否则将异常分发给此线程所在的线程组。
1 | /** |
分别来看下两种方式:
线程自己处理
Thread类有一个uncaughtExceptionHandler属性,表示这个线程当这个线程发生未捕获异常时的处理器,可以通过Thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler方法来设置这个属性。如果没有显式调用此方法设置,那么uncaughtExceptionHandler属性默认为null。
1 | // null unless explicitly set |
交给线程组处理
如果没有设置线程的uncaughtExceptionHandler属性或者为null,则会将异常信息分发给线程所在的线程组。上面代码可以将group作为结果返回是因为所有线程组的父类ThreadGroup类实现了Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler接口。
如果当前线程的线程组重写了uncaughtException方法,会调用重写的uncaughtException方法,否则调用ThreadGroup类的uncaughtException方法。
下面是这个ThreadGroup类的uncaughtException方法的实现:
1 | /** |
处理流程如下:
- 首先,如果这个线程组有父线程组(
parent属性),将会调用父线程组的uncaughtException方法处理。 - 否则,先调用
Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()检查是否有一个默认的UncaughtExceptionHandler,如果有,交给这个默认的UncaughtExceptionHandler来处理。 - 否则,如果该异常是
ThreadDeath的实例,那么直接退出,如果不是,会将线程名字以及异常栈打印至标准错误输出流(控制台)。这是我们没有设置任何处理器时的默认逻辑,开头那段代码就是这种情况,没有设置任何处理器,所以只是在控制台输出了线程名称和异常信息。
默认处理器
上面代码中第二个分支中Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()是什么呢?
1 | // null unless explicitly set |
可以看到这个方法是一个Thread类的静态方法,defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler也是Thread类的静态属性,表示可以供所有线程使用的默认的UncaughtExceptionHandler。可以分别通过setter方法和getter方法设置和获取。
处理流程总览
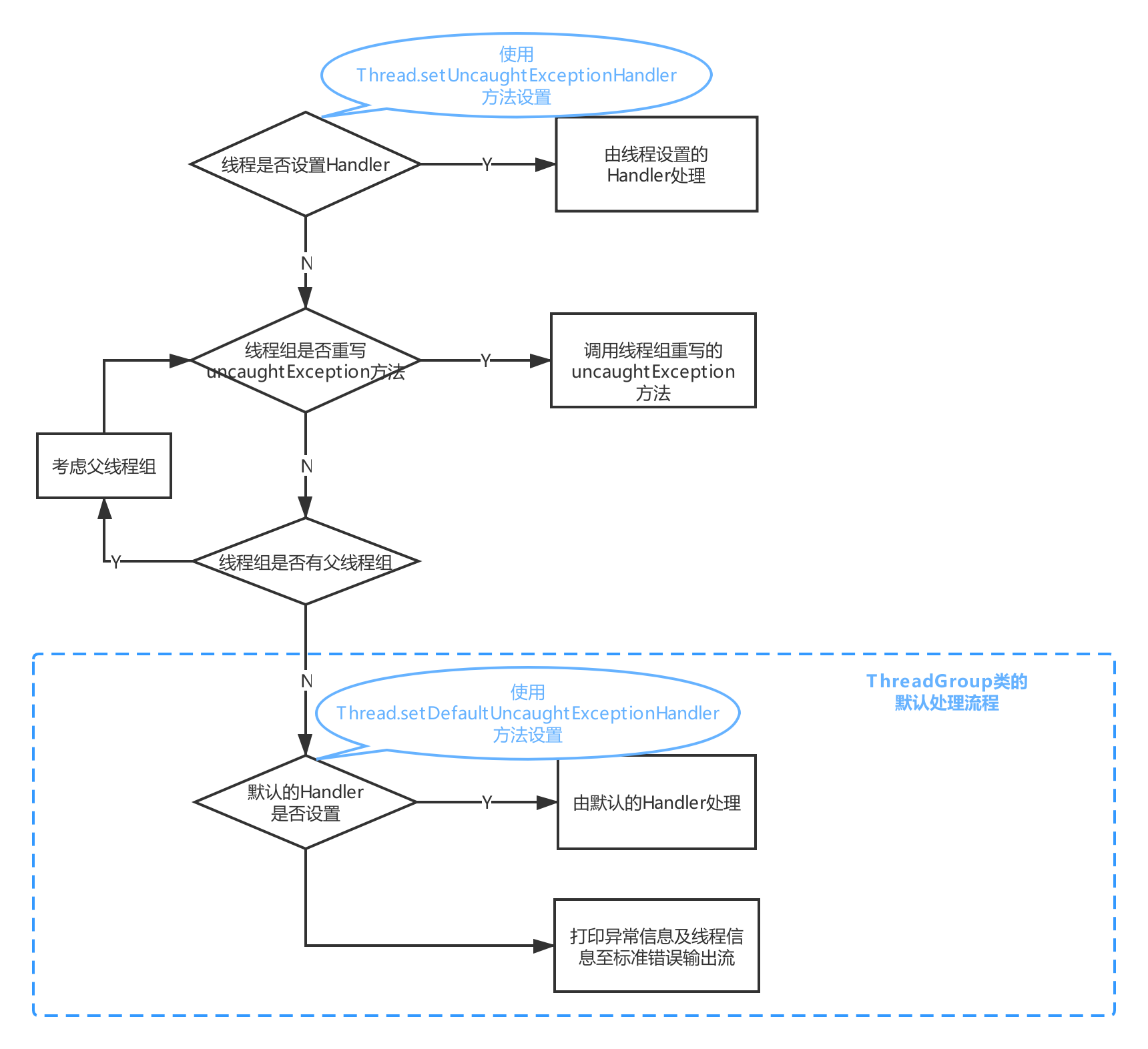
注:上图中Handler指的是
UncaughtExceptionHandler
扩展知识
ThreadGroup - 线程组
- 线程组是一组线程的集合
- 线程组中也可以包含其他线程组
- 线程组的组织是一个树结构,除了初始线程组之外每个线程组都有父线程组
- 线程组实现了
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler接口 - 初始线程组是
system线程组,由系统创建,这个线程组没有父线程组,通过下面这个构造方法创建1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/**
* Creates an empty Thread group that is not in any Thread group.
* This method is used to create the system Thread group.
*/
private ThreadGroup() { // called from C code
this.name = "system";
this.maxPriority = Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;
this.parent = null;
}
ThreadDeath
我们还忽略了一个小细节,就是在ThreadGroup类的默认处理逻辑中,如果异常是ThreadDeath的实例,是不会进行处理的。ThreadDeath的源码:
1 | /** |
当Thread.stop()方法被调用时,会抛出一个ThreadDeath类的实例。
应用程序只有必须在异步终止后进行清理时才应该捕获该类的实例。如果 ThreadDeath 被一个方法捕获,那么将它重新抛出非常重要,因为这样才能让该线程真正终止。
这就是为什么ThreadGroup的uncaughtException没有捕获ThreadDeath异常。